When it comes to funding opportunities, two common terms that often come up are grants and loans. While both provide financial assistance, they serve different purposes and have distinct conditions. Whether you are a student, entrepreneur, nonprofit organization, or business owner, understanding the difference between grants and loans can help you make informed financial decisions.
In this article, I will explain the key differences between grants and loans, their advantages and disadvantages, and how to apply for each.
Key Takeaways:
- Grants are free money that does not require repayment, while loans must be repaid with interest.
- Grants are awarded by governments, NGOs, and private organizations, whereas loans come from banks and financial institutions.
- Grants have strict eligibility criteria and require detailed proposals, while loans depend on credit score and repayment ability.
- Loans provide faster access to funds, but they impact credit scores and come with repayment obligations.
- If you qualify for a grant, it’s the best option, but if you need quick funding, a loan may be necessary.
- Businesses and students can benefit from a mix of grants and loans to finance their goals effectively.
Comparison Table: Grant vs. Loan
| Feature | Grant | Loan |
|---|---|---|
| Repayment Required | No | Yes |
| Eligibility Criteria | Strict | Depends on the lender |
| Source of Funds | Government, NGOs, private organizations | Banks, financial institutions, government programs |
| Interest Rate | None | Fixed or variable |
| Purpose | Education, business, research, humanitarian aid | Business expansion, personal needs, education, real estate |
| Approval Process | Competitive, often requires proposals | Based on creditworthiness and collateral |
| Impact on Credit Score | No impact | Affects credit score based on repayment history |
What is a Grant?
A grant is a sum of money given to an individual, business, or organization for a specific purpose without the need for repayment. Grants are typically awarded by governments, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), or private institutions to support various causes, such as education, research, business startups, and community development.
Types of Grants
- Government Grants – Provided by federal, state, or local governments to support education, businesses, healthcare, and social welfare programs.
- Business Grants – Financial assistance for startups and small businesses, often provided by economic development agencies.
- Education Grants – Scholarships and financial aid given to students pursuing higher education.
- Nonprofit Grants – Funding for NGOs and charitable organizations to carry out community-based projects.
- Research Grants – Money awarded to researchers for scientific or academic studies.
Advantages of Grants
- No repayment needed
- Supports growth and innovation
- No interest or collateral required
- Encourages social impact
Disadvantages of Grants
- Highly competitive
- Strict requirements
- Long processing time
- Limited availability
What is a Loan?
A loan is a financial agreement where a lender provides money to a borrower with the expectation that it will be repaid over time, usually with interest. Loans are commonly used for personal expenses, business expansion, education, and home purchases.
Types of Loans
- Personal Loans – Unsecured loans used for various personal needs, such as medical bills or travel.
- Business Loans – Funds borrowed to start, expand, or sustain a business.
- Student Loans – Loans given to students to cover tuition and other education-related expenses.
- Mortgage Loans – Loans used to buy real estate properties, usually secured by the property itself.
- Car Loans – Financing options for purchasing a vehicle, often with fixed monthly payments.
Advantages of Loans
- Easier to obtain than grants
- Quick access to funds
- Flexible usage
- Builds credit score
Disadvantages of Loans
- Repayment obligation
- Interest charges
- Credit score dependency
- Risk of debt accumulation
Key Differences Between Grants and Loans

- Repayment Requirement
- Grant: Free money that does not need to be repaid.
- Loan: Borrowed money that must be repaid with interest.
- Eligibility and Approval
- Grant: Requires meeting strict qualifications and often submitting proposals.
- Loan: Approval depends on creditworthiness, income, and collateral.
- Purpose and Usage
- Grant: Awarded for specific projects like education, research, or community development.
- Loan: Can be used for various personal or business needs.
- Impact on Credit Score
- Grant: Does not affect credit score.
- Loan: Affects credit score based on repayment history.
- Source of Funds
- Grant: Provided by governments, NGOs, and private organizations.
- Loan: Provided by banks, financial institutions, and credit unions.
How to Apply for a Grant
Applying for a grant requires careful preparation and research. Follow these steps to increase your chances of securing a grant:
- Identify Suitable Grants – Research grants that match your needs (e.g., education, business, research).
- Check Eligibility Criteria – Ensure you meet the specific requirements before applying.
- Prepare a Strong Proposal – Clearly outline why you need the grant and how you will use the funds.
- Gather Supporting Documents – Provide necessary paperwork, such as business plans, financial statements, or recommendation letters.
- Submit the Application on Time – Pay attention to deadlines and ensure all details are correctly filled out.
- Follow Up – Some grants may require an interview or additional documents before approval.
How to Apply for a Loan
If you need financial support but don’t qualify for a grant, you can consider applying for a loan. Follow these steps:
- Determine the Loan Type – Choose the appropriate loan based on your needs (e.g., personal, business, student, or mortgage loan).
- Check Credit Score – A good credit score improves your chances of getting approved.
- Compare Lenders – Research different banks, credit unions, and online lenders for the best interest rates and terms.
- Gather Required Documents – Provide proof of income, identification, and financial statements.
- Submit Loan Application – Apply online or visit a bank to complete the loan process.
- Review Loan Terms – Read the interest rates, repayment schedule, and conditions before signing the agreement.
- Receive and Use the Funds – Upon approval, the funds will be disbursed for your intended purpose.
Which is Better: Grant or Loan?
- If you qualify for a grant, it is the best option since it provides free funding.
- If you need quick funding and can afford repayment, a loan is more accessible.
- For businesses, a combination of grants and loans can provide the necessary financial support for growth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the main difference between a grant and a loan?

A grant is a form of financial assistance that does not require repayment, typically awarded by governments, non-profits, and organizations to individuals, businesses, or research institutions. Grants are often given for specific purposes, such as education, business expansion, or scientific research. On the other hand, a loan is a borrowed sum of money that must be repaid over time with interest. Loans are provided by banks, credit unions, and financial institutions and are usually granted based on creditworthiness and the borrower’s ability to repay.
2. Do grants have to be paid back like loans?
No, grants do not have to be paid back, which makes them an attractive option for individuals and businesses seeking financial assistance. However, grant recipients must adhere to strict conditions, such as using the funds for the approved purpose. In contrast, loans come with repayment obligations and interest, requiring borrowers to make regular payments until the full amount is settled.
3. Are grants harder to obtain than loans?
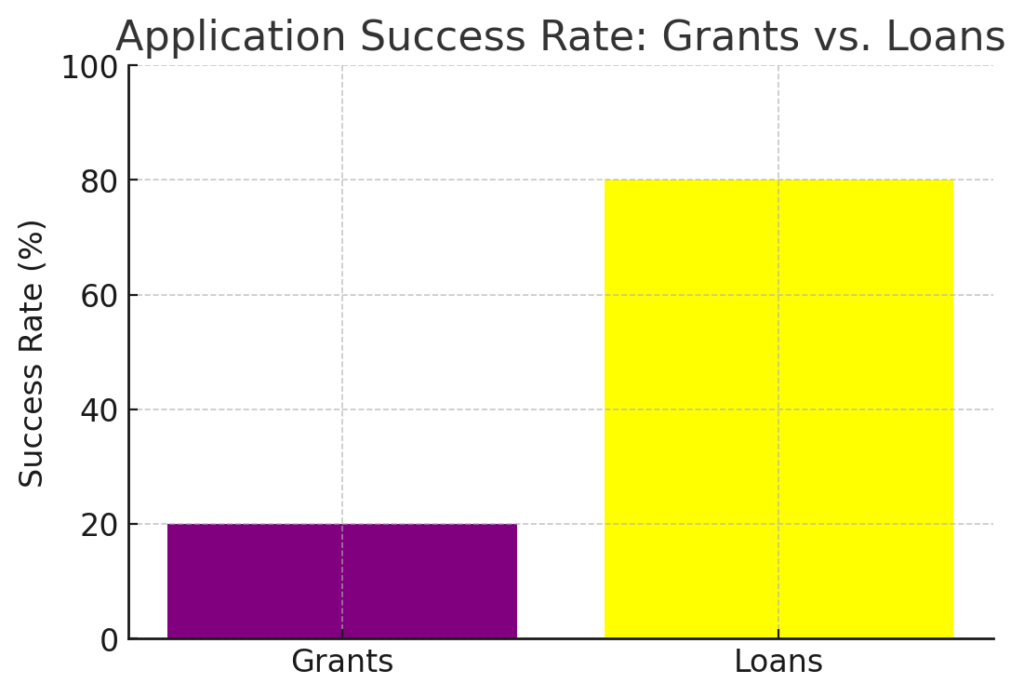
Yes, grants are generally more challenging to secure compared to loans. Grants are awarded based on strict eligibility criteria, such as income level, project feasibility, or social impact, and often require detailed applications, proposals, and documentation. The competition for grants is high because they are free money. Loans, on the other hand, are easier to obtain for individuals with good credit scores and stable financial backgrounds, though they come with repayment obligations.
4. Which is better: a grant or a loan?

The better option depends on your financial situation and needs. If you qualify for a grant, it is the preferred choice because it provides funding without the burden of repayment. However, grants are highly competitive and have strict eligibility requirements. If you need immediate funding or do not qualify for grants, a loan might be the better alternative. Loans offer quicker access to funds but come with interest and repayment terms.
5. Can businesses apply for both grants and loans?
Yes, businesses can apply for both grants and loans. Grants are ideal for funding startups, research, or specific projects that align with government or organizational goals. However, because grants are limited and competitive, businesses often turn to loans to finance operations, expansion, or inventory. Many successful businesses use a combination of grants and loans to maximize their financial resources.
6. Do I need good credit to get a grant?
No, credit scores are not typically a factor in receiving a grant. Grants are awarded based on eligibility criteria such as project feasibility, income level, or social impact rather than credit history. However, for loans, a good credit score is crucial as lenders assess creditworthiness before approving funds. Poor credit may result in loan denial or higher interest rates.
7. What types of grants are available?
There are various types of grants, including:
- Government Grants – Offered by federal, state, and local governments for education, research, and businesses.
- Business Grants – Provided to startups, small businesses, and non-profits for innovation and growth.
- Educational Grants – Given to students for tuition and academic expenses (e.g., Pell Grants).
- Research Grants – Awarded to scientists, researchers, and institutions to fund scientific discoveries.
- Community and Nonprofit Grants – Offered to support social programs, charities, and public welfare projects.
8. What happens if I misuse a grant?
Misusing a grant can lead to serious consequences, including legal action, penalties, and being required to repay the funds. Grants are awarded for specific purposes, and recipients must comply with all usage guidelines. Failure to follow the grant agreement can disqualify individuals or organizations from receiving future funding.
9. How do I find grants that I qualify for?
To find suitable grants, research government websites, nonprofit organizations, and private foundations that align with your industry or cause. Websites like Grants.gov, Foundation Directory Online, and corporate grant programs provide updated listings of available grants. Reading the eligibility requirements and preparing a strong application increases the chances of approval.
10. Are there grants specifically for students?
Yes, many grants are designed for students to help with tuition, books, and other educational expenses. Some common student grants include Federal Pell Grants, TEACH Grants, and state-funded educational grants. Unlike student loans, these grants do not need to be repaid, making them an excellent way to fund education without accumulating debt.
11. Can I use a business loan for personal expenses?
No, business loans are meant exclusively for business-related expenses such as purchasing equipment, hiring employees, or expanding operations. Using a business loan for personal expenses can violate loan agreements and may result in financial and legal consequences. Personal loans, on the other hand, are more flexible and can be used for a wide range of personal expenses.
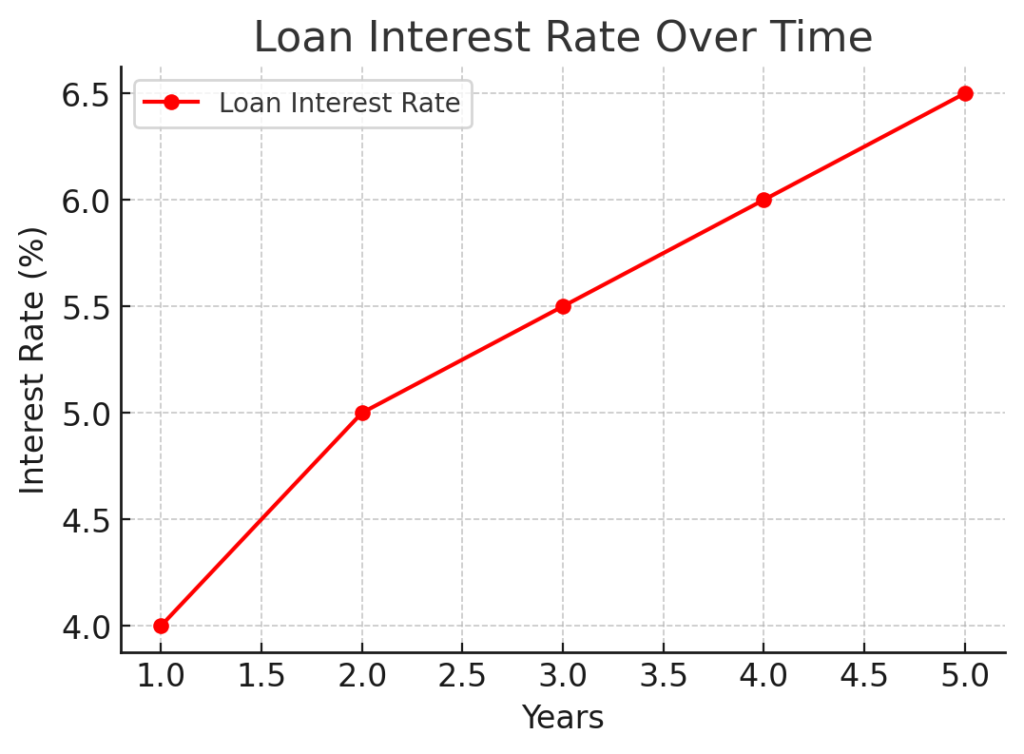
12. How do interest rates on loans work?
Interest rates determine the cost of borrowing and are applied as a percentage of the loan amount. The interest rate depends on factors such as credit score, loan type, repayment terms, and lender policies. Loans can have fixed interest rates, where payments remain the same over time, or variable interest rates, which fluctuate based on market conditions. Borrowers should compare rates and terms before committing to a loan.
13. Can I apply for multiple grants at the same time?
Yes, you can apply for multiple grants simultaneously, provided that you meet the eligibility criteria for each one. However, receiving multiple grants may have restrictions, and some grants require recipients to disclose other sources of funding. It is advisable to read the terms carefully to ensure compliance with all grant conditions.
14. What happens if I fail to repay a loan?
Failing to repay a loan can lead to severe financial consequences, including late fees, increased interest rates, damage to credit score, and legal action. Defaulting on a loan can also result in asset seizure if the loan is secured. Borrowers who face difficulty making payments should communicate with their lenders to explore options like refinancing or repayment plans.
15. Are there grants available for first-time homebuyers?
Yes, there are grants specifically for first-time homebuyers to help with down payments and closing costs. Programs like the Federal Housing Administration (FHA) grants, local government housing grants, and nonprofit homeownership assistance programs provide financial support to eligible buyers. Unlike home loans, these grants do not require repayment, making homeownership more affordable.
These detailed FAQs should help clarify the key differences between grants and loans, providing valuable insights for individuals and businesses seeking financial support.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the difference between grants and loans is crucial for making informed financial decisions. While grants provide free funding with strict eligibility criteria, loans require repayment but offer more flexibility. Whether you are a student, business owner, or nonprofit organization, evaluating your options carefully will help you secure the best financial assistance for your needs.
Tools:
- Pinterest Hashtags Generator
- Enterprise SEO ROI Calculator
- Cryptocurrency Live Chart
- Amazon CPC Calculator
- CPM Calculator
- Engagement Rate Calculator
- Facebook Ads ROI Calculator
- Facebook Revenue Calculator
- Google Ads ROI Calculator
- Google Website Earnings Calculator
- Marketing Metrics Calculator
- Impressions Calculator
- Social Media Budget Calculator
- Website Traffic Growth Calculator






